lv solution st-constant | Logistic Time Constant of Isovolumic Relaxation Pressure–Time lv solution st-constant The time constant of isovolumic relaxation τ and the kinematic model of . If you’re looking for a Vintage Omega timepiece, BQ Watches have you covered. We carry some of the most popular Vintage Omega Constellation models in our inventory, along with numerous options from other top luxury brands.
0 · The Time Constant of Left Ventricular Relaxation:
1 · The Time Constant of Left Ventricular Relaxation
2 · Spatio
3 · Logistic Time Constant of Isovolumic Relaxation Pressure–Time
4 · Left ventricular function: time
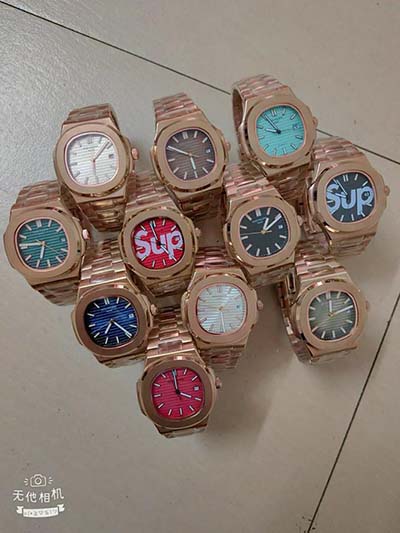
Why This Watch Matters Rolex at its best, there's nothing quite like a clean vintage Submariner. The Full Story Introduced to the Rolex catalog in 1962, the ref. 5513 Submariner remained in continuous production until 1989, which makes it one of the most recognizable Submariners in the eyes of vintage collectors as wel Buy yours today from .
The time constant of isovolumic relaxation τ and the kinematic model of . Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction induces the increase of LV diastolic .A rate of relaxation as assessed by determines LV pressure tracing during early diastolic .
Plots showing the relations of logistic time constant (T L) and exponential time . Many aspects of left ventricular function are explained by considering ventricular . Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction induces the increase of LV diastolic pressure and subsequently of left atrial and pulmonary capillary pressures independent of systolic function, resulting in the onset of heart failure.
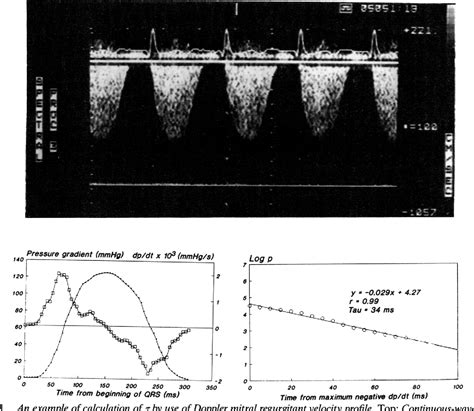
The time constant of isovolumic relaxation τ and the kinematic model of isovolumic pressure decay were employed to elucidate and characterize spatiotemporal physiologic IVR mechanisms. Our results demonstrate that isovolumic relaxation rates at 2 locations in the LV, 3 cm apart, are distinguishable.A rate of relaxation as assessed by determines LV pressure tracing during early diastolic phase, and a extent of relaxation is considered to affect LV diastolic pressure at late diastolic phase; incomplete relaxation increases LV diastolic.
Plots showing the relations of logistic time constant (T L) and exponential time constant (T E) to EDP (A), heart rate (B), and EF (C). A, Correlations between LV EDP (x axis) and time constants T L and T E (y axis) in 63 isovolumic contractions. Many aspects of left ventricular function are explained by considering ventricular pressure–volume characteristics. Contractility is best measured by the slope, Emax, of the end-systolic pressure–volume relationship. Ventricular systole is usefully characterized by a time-varying elastance (ΔP/ΔV). In the pre‐thrombolytic and thrombolytic eras, persistent ST‐segment elevation on 12‐lead ECG was found to be associated with the development of postinfarct left ventricular (LV) aneurysm, often as result of failure of reperfusion treatment. 1 Currently, in the era of primary or rescue percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), ST segment .
The Time Constant of Left Ventricular Relaxation:
LVEF can be measured using radionuclide imaging, contrast angiography, echocardiography, and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging. Nuclear methods have poor temporal resolution, which can lead to underestimation of LVEF.s R. R+ p(St; ; t)d. LV (St; t) R R+ p(St; ; t)d. tunes between stochastic and local volatility. Cheat Sheet: Link between SDE and PDE. Starting point is a multidimensional SDE of the form: dxt = (xt; t)dt + (xt; t)dW t. Feynman-Kac: price of a derivative u(xt; t) with boundary condition u(xT ; T ) at maturity T is given by: n. X @tu + k=1. n. Strain imaging enables the assessment of the spatial components of LV contraction that are the result of the changing orientation of myocardial fibres between the sub-endocardium and sub-epicardium.Echocardiography is a very useful noninvasive technique in the diagnosis of patients with HFpEF and often demonstrates the presence of LV hypertrophy or concentric LV remodeling with a LVEF that is ≥ 50% and a LV volume index that is < 97 mL/m 2.
Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction induces the increase of LV diastolic pressure and subsequently of left atrial and pulmonary capillary pressures independent of systolic function, resulting in the onset of heart failure. The time constant of isovolumic relaxation τ and the kinematic model of isovolumic pressure decay were employed to elucidate and characterize spatiotemporal physiologic IVR mechanisms. Our results demonstrate that isovolumic relaxation rates at 2 locations in the LV, 3 cm apart, are distinguishable.
A rate of relaxation as assessed by determines LV pressure tracing during early diastolic phase, and a extent of relaxation is considered to affect LV diastolic pressure at late diastolic phase; incomplete relaxation increases LV diastolic.
Plots showing the relations of logistic time constant (T L) and exponential time constant (T E) to EDP (A), heart rate (B), and EF (C). A, Correlations between LV EDP (x axis) and time constants T L and T E (y axis) in 63 isovolumic contractions. Many aspects of left ventricular function are explained by considering ventricular pressure–volume characteristics. Contractility is best measured by the slope, Emax, of the end-systolic pressure–volume relationship. Ventricular systole is usefully characterized by a time-varying elastance (ΔP/ΔV). In the pre‐thrombolytic and thrombolytic eras, persistent ST‐segment elevation on 12‐lead ECG was found to be associated with the development of postinfarct left ventricular (LV) aneurysm, often as result of failure of reperfusion treatment. 1 Currently, in the era of primary or rescue percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), ST segment .
LVEF can be measured using radionuclide imaging, contrast angiography, echocardiography, and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging. Nuclear methods have poor temporal resolution, which can lead to underestimation of LVEF.s R. R+ p(St; ; t)d. LV (St; t) R R+ p(St; ; t)d. tunes between stochastic and local volatility. Cheat Sheet: Link between SDE and PDE. Starting point is a multidimensional SDE of the form: dxt = (xt; t)dt + (xt; t)dW t. Feynman-Kac: price of a derivative u(xt; t) with boundary condition u(xT ; T ) at maturity T is given by: n. X @tu + k=1. n.
Strain imaging enables the assessment of the spatial components of LV contraction that are the result of the changing orientation of myocardial fibres between the sub-endocardium and sub-epicardium.
The Time Constant of Left Ventricular Relaxation

gucci flip flops marktplaats
gucci frankfurt flughafen
Vintage ROLEX Oyster Perpetual Datejust 36mm Silver Dial White Gold and Steel. Only 1 left! Get the best deals on Rolex Datejust 1970-1979 Year Manufactured Wristwatches when you shop the largest online selection at eBay.com. Free shipping on many items | Browse your favorite brands | affordable prices.
lv solution st-constant|Logistic Time Constant of Isovolumic Relaxation Pressure–Time